Design custom products with Printify
Have you ever wondered why the colors on your computer screen look different when printed? Understanding the difference between RGB vs CMYK is fundamental for achieving accurate and vibrant print results.
Let’s break down these two color models.
Key takeaways
- Understand the difference between RGB and CMYK. RGB is for digital screens, while CMYK is for print.
- Choose the appropriate file format based on image complexity and desired output. PDF is versatile, TIFF is ideal for high-resolution images, EPS is best for vector graphics, and AI is for complex Adobe Illustrator designs.
- Convert RGB files to CMYK for accurate print results. While it’s possible to print RGB images, converting to CMYK ensures better color accuracy when printing.
- Sample your products. Order physical samples to see how colors appear in print before launching your store.
- Understand the limitations of CMYK. Printed colors may appear less vibrant than they do on screen due to ink color and material constraints. Manage expectations by adjusting designs and color channels accordingly for optimal print results.
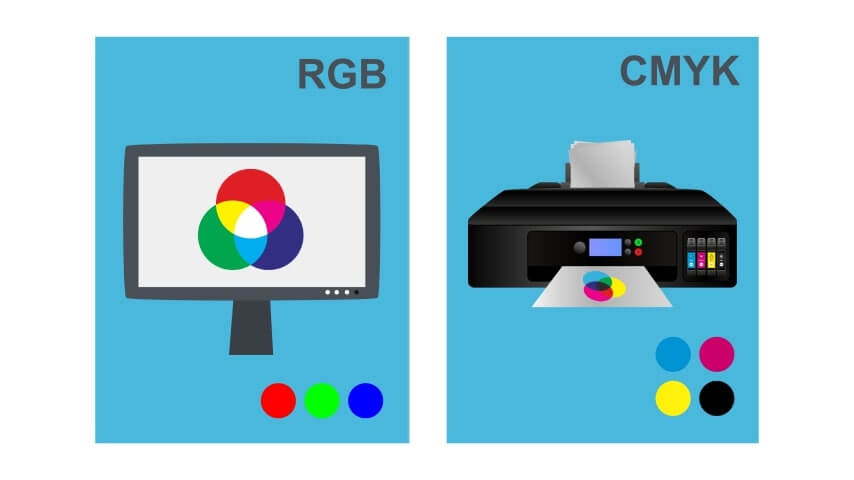
RGB vs CMYK: What’s the difference?
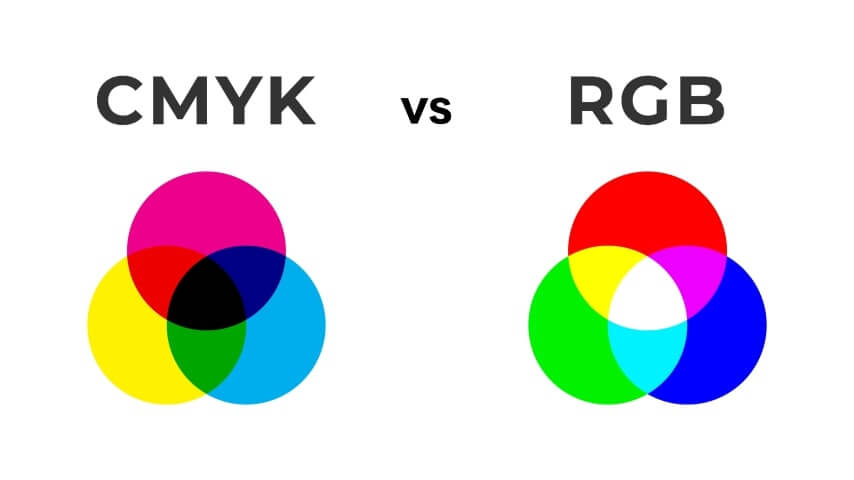
RGB and CMYK are two primary color models, or color spaces, used in graphic design.
The RGB color mode is used mainly for electronic displays such as computer monitors, smartphones, and TVs.
The RGB color space has a wider gamut (range of colors) than CMYK – meaning you can create more vibrant and saturated colors on a screen using RGB. It’s ideal for creating vibrant and eye-catching graphics for websites, social media, and digital marketing materials.
CMYK, on the other hand, is used mostly for printed materials.
The CMYK color space has a narrower gamut due to the limitations of ink technology. This is why printed colors often appear less vibrant than their digital counterparts.
However, this color mode is essential for accurate color reproduction in print, such as brochures, posters, magazines, and product packaging.
Understanding the differences between these color modes will help you achieve consistent, high-quality results across both digital and print media and products.
What is RGB?

RGB stands for red, green, and blue – this model creates hues by combining these three primary colors. It’s an additive process that starts with black and builds color through increasing light intensity.
It’s possible to control aspects like vibrancy, saturation, and shading by adjusting the RGB colors. Because this process is entirely digital, you can manipulate how the light on the screen combines to create the desired color.
When is RGB used?
In short, RGB is used for all things digital. This includes visual content like videos and photos, web and app design, icons, graphics, and buttons. It also applies to branding elements like logos, ads, and banners, as well as social media-related features like profile pictures, cover photos, images for posts, and others.
Nearly every computer and mobile device uses the RGB color system to represent colors effectively and efficiently on your screen. Red, green, and blue are coded in a language that computers understand – using bits. However, due to technical limitations, the RGB color gamut (the range of colors for color space) is smaller than what the human eye can perceive.
What are the best file formats for RGB?
Choose the right file type to achieve accurate print colors. The most common formats for RGB images are:
- JPEG: This format is widely used for its balance between file size and image quality. It’s suitable for most types of digital images, especially photographs.
- GIF: Best used for images with limited color palettes and animations, GIFs are ideal for web graphics but are less suitable for high-resolution prints.
- PNG: A lossless format that supports transparency, making it perfect for images requiring clear backgrounds. PNG is great for web use and images with sharp edges.
- SVG: Ideal for vector graphics, SVG brings scalability without losing quality. It’s widely used for logos, icons, and illustrations, especially in web design.
While these formats are generally preferred, checking with your specific printer to confirm their requirements and recommended file types is always recommended.
Explore more about color profiles, RGB values, and how to create colors and designs in our Must-Read Design Guide.
What is CMYK?

CMYK colors are created by mixing cyan, magenta, yellow, and pure black inks. Unlike RGB, this is a subtractive process where color is produced by removing natural white light from a medium. More ink equals darker colors.
When all the colors are mixed together in the CMYK mode, they produce a dark, muted color. Black ink is added separately to achieve a deeper black and enhance image contrast.
Did you know? CMYK stands for cyan, magenta, yellow, and key. Key is the area where these colors align and produce black by mixing tiny dots of ink.
When is CMYK used?
CMYK is used for any design project that’s physically printed instead of viewed on a screen. So, if you need to recreate the design you see on screen with ink, the CMYK color model will provide more accurate results.
This includes all things branding: business cards, custom stickers, stationery, store signs, etc. Additionally, everything related to advertising: posters, flyers, billboards, booklets, and merchandise. Personalized t-shirts, totes, hats, and other apparel and accessories are created using CMYK color modes.
What are the best file formats for CMYK?
Using the appropriate file formats for your project can significantly enhance color accuracy and print quality.
Here are the most suitable options for CMYK files:
- PDF: This versatile format preserves color profiles, ensuring accurate color reproduction. PDFs can handle both vector and raster graphics, making them suitable for complex designs.
- TIFF: Ideal for high-resolution images, TIFF is a lossless format that maintains image quality without compression. This is particularly beneficial for photographs and detailed graphics.
- EPS: Primarily used by vector programs, EPS ensures scalability without compromising image clarity. This format is perfect for logos, illustrations, and designs that need to be resized without pixelation.
- AI: As Adobe Illustrator’s native format, AI offers maximum editing flexibility and preserves all design elements, including layers and effects. This is the preferred choice for complex vector-based artwork.
RGB vs CMYK: Which one should you use for design files?

RGB is ideal for digital images and scenarios where color printing isn’t a concern. However, if you’re deciding between CMYK and RGB for printing, CMYK is generally the better choice.
The CMYK mode provides a more reliable reproduction of colors in the final print compared to what you see on a digital screen. When you convert RGB-mode files to CMYK to print on a four-color printer (which is the majority of printers), there are differences between the same colors.
These shifts are usually minor, but they can still be an issue, especially if your design project is color-sensitive. Similarly, if you upload a CMYK image to the Internet, you may also see differences in the color space.
Can RGB images be printed?

While it’s technically possible to print RGB images, it’s not recommended.
Most printers are designed to work with CMYK color mode, which is specifically tailored for print production. Converting an RGB image to CMYK during the printing process can lead to color alteration and a loss of vibrancy.
To achieve the best possible print results, it’s highly recommended to design your images in CMYK from the start. This gives you more control over color accuracy and ensures your printed piece matches your vision.
However, there are some exceptions. High-end printers and specific printing processes might be able to handle RGB images directly, but it’s always best to consult with your printer to confirm their capabilities and select the desired color space.
Explore the best printing methods for your merch on our blog.
How to set up RGB vs CMYK color modes in design programs

Be sure to work in the correct color mode from the beginning of your design process. Converting between RGB and CMYK can lead to color changes, so it’s generally recommended to start with the appropriate color mode for your project.
Here’s how to do it:
Photoshop
- Creating a new document: When starting a new project, navigate to File > New. Under Color Mode, select either RGB or CMYK, depending on your project’s intended use.
- Converting an existing image: If you have an existing RGB image and need to convert it to CMYK, go to Image > Mode and select CMYK. Be aware that this conversion might result in color shifts. Click on Flatten image to keep the image’s overall appearance.
Illustrator
- Creating a new document: Similar to Photoshop, when creating a new document, choose the desired color mode (RGB or CMYK) under the Color Mode option.
- Converting an existing document: To change the color mode of an existing Illustrator file, go to File > Document Color Mode and select the desired color mode.
How to convert RGB to CMYK?
If you’ve created your design in RGB, you can preview how it might look when printed by converting it to CMYK. This will give you a rough estimate of the color shift. Here’s how to do it:
Photoshop
Before creating the art file click Image > Mode > CMYK Color.
Illustrator
Before creating the art file, click File > Document Color Mode > CMYK Color.
If you don’t have access to any design software, use the CMYK preview feature in our Product Creator for more realistic previews.
If you’re downloading images and graphics from an online resource (make sure they’re royalty-free!), don’t forget to convert that image to CMYK (and make sure it’s hi-res to ensure high-quality print). However, this doesn’t mean that all your designs need to be converted to CMYK. If your customers want to see the actual representation of the colors, then the CMYK color palette is the closest to reality.
How to make sure your print colors are what you want them to be

Before launching your online store, order samples of your products. This allows you to assess the actual print colors and overall product quality. Color vibrancy can vary significantly between materials, so seeing the final product firsthand is crucial for avoiding customer dissatisfaction.
Sampling also allows you to showcase your products with personalized videos and build excitement for your brand.
How to get bright print colors with CMYK
While RGB offers a vast color spectrum, CMYK has its limitations. Due to the nature of inks and materials, printed colors often appear less vibrant than their digital counterparts. Solid colors created by combining 100% cyan, magenta, and yellow tend to be the most vivid in print. However, even these will be less bright than on a screen.
It’s important to note that various materials absorb and reflect light differently, affecting color appearance. For instance, a cotton hoodie will produce less vibrant colors than a PU leather product.
To achieve the desired color in print, you may need to adjust your design. Tinting colors can help, but keep in mind that CMYK is less effective at creating subtle shades than the RGB color model. Understand these constraints and manage expectations to achieve the best possible print results.
Apply your print design on products with Printify
Printify is an excellent way to get started. It’s free for everyone, regardless of the size of your online business. Sign up, design merchandise from our vast Catalog of over 900 customizable products, and integrate with the most popular eCommerce platforms and marketplaces.
We can’t talk about designing products without mentioning the Product Creator (formerly known as the Mockup Generator), where you can use your newly acquired knowledge about print colors. It’s super easy to use and generates stunning product mockups to add to your online storefront.
How to achieve the best possible results
Unless you’re a corporation with a strict brand book, there really is no point in spending excessive time on color calibration or management. All you need to do is make sure that what your customers see on their mobile or computer screens is as close as possible to the actual print colors they’ll receive.
Which color profile should you use for your files? Find out more in our Help Center.
FAQ: CMYK vs RGB printing
It depends on your project. The RGB color model is best for digital devices like computer and smartphone screens.
What color model is used in printed designs? CMYK is specifically used for printing.
Yes, converting your RGB file to CMYK is generally recommended before sending it to print. This ensures accurate color reproduction. However, some printers can handle the RGB model, so it’s best to check with your specific printer.
RGB and CMYK use different color models. RGB is an additive color model, meaning colors are created by combining red, green, and blue light. CMYK is a subtractive color model, where colors are created by subtracting white light from a surface by using cyan, magenta, yellow, and black ink.
This fundamental difference leads to variations in color appearance between digital screens and printed materials. Is CMYK or RGB better for printing? CMYK is the more realistic choice.
Conclusion
Now you know the difference between RGB and CMYK. Armed with this knowledge, start designing your own products to sell on your online store. Printify makes bringing your designs to life easy with over 900 print-on-demand products and more than 80 global Printing Partners.
Let your creativity shine!












