Start a print-on-demand business today
When you’ve worked hard to create stunning visuals for your brand, protecting it should be a top priority. That’s where copyright and trademark rights come into play.
This article will show you how to copyright a logo and explain why trademarking your brand helps provide enhanced protection in the marketplace.
Key takeaways
- Copyrighting safeguards the creative design of your company’s logo, while a trademark protects its association with your business in the marketplace, helping to prevent confusion with similar logos.
- It’s important to copyright and trademark a logo to stop others from copying or misusing it. This provides legal protection and gives you leverage if infringement occurs.
- You can copyright your logo with the United States Copyright Office and file a trademark application with the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO). Both processes are available online.
- To enforce your rights, monitor your business logo for unauthorized use. If you spot infringement, gather evidence and consult a trademark attorney to take necessary action, such as sending a desist letter or pursuing legal options in federal court.
- Copyright applies to creative works like logos, drawings, and software code, while trademarks protect brand elements like logos, names, slogans, and packaging. You cannot copyright ideas, methods, and common knowledge.
The statements provided in this article are for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as professional or legal advice. Always consult with a qualified professional or legal advisor for any specific questions or concerns you may have.
What is copyright?

Copyright gives you the exclusive rights to control how your original work is used and shared.
Once your logo is fixed in a tangible medium (written, recorded, or saved in digital form), you automatically claim copyright ownership. This means you decide who can legally use, reproduce, or display your work.
With digital piracy causing $29.2 billion in losses in the US annually, having this protection is more important than ever.
While your logo gets automatic copyright protection, registering it through the United States Copyright Office gives you stronger rights to take legal action. As the registeredcopyright owner, you have more control to stop others from copying or using your work without permission.
What is a trademark?

A trademark protects the unique logos, symbols, names, phrases, or designs that are identifiable to your brand. It safeguards your brand’s identity and recognition.
As a trademark owner, you get exclusive rights to use your logo and other brand elements in commerce, preventing others from using similar logos that might confuse your customers.
Registering your trademark through the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) provides nationwide protection. You can also safeguard your brand internationally through the Madrid Protocol.
Trademark vs copyright: What’s the difference?
Both copyright and trademark laws are essential for protecting your intellectual property rights, but they cover different aspects of your brand.
Copyright automatically protects your logo as original artistic work, giving you exclusive rights to reproduce and distribute it. However, copyright doesn’t cover the brand identity linked to your logo.
That’s where trademark law comes in. The trademark status protects identifiable elements of your brand, like your unique logo, designs, or slogans, and prevents others from using anything similar that might confuse customers.
Using copyright and trademark as intellectual property protection for your logo helps safeguard your brand creatively and commercially.
Logos are not always eligible for copyright protection if they lack sufficient originality or creativity – for example, logos with only text or simple geometric shapes.
What can you safeguard with copyright protection?
- Artistic works: Logos, paintings, drawings, and photographs that exhibit creativity.
- Literary works: Books, articles, and other written content.
- Musical compositions: Original music and lyrics.
- Audiovisual works: Films, videos, and animations.
- Software code: Original programming and applications.
What can you safeguard with trademark protection?
- Business logo: Unique designs that visually represent your brand.
- Brand name: The name that identifies your products or services.
- Slogans: Catchphrases or taglines associated with your brand.
- Product packaging: Specific designs or shapes that distinguish your products.
- Sounds, scents, and colors: Unique auditory or sensory elements that are strongly linked to your brand identity.
Trademark and copyright symbols
Works protected by copyright or trademark are marked with the following symbols.
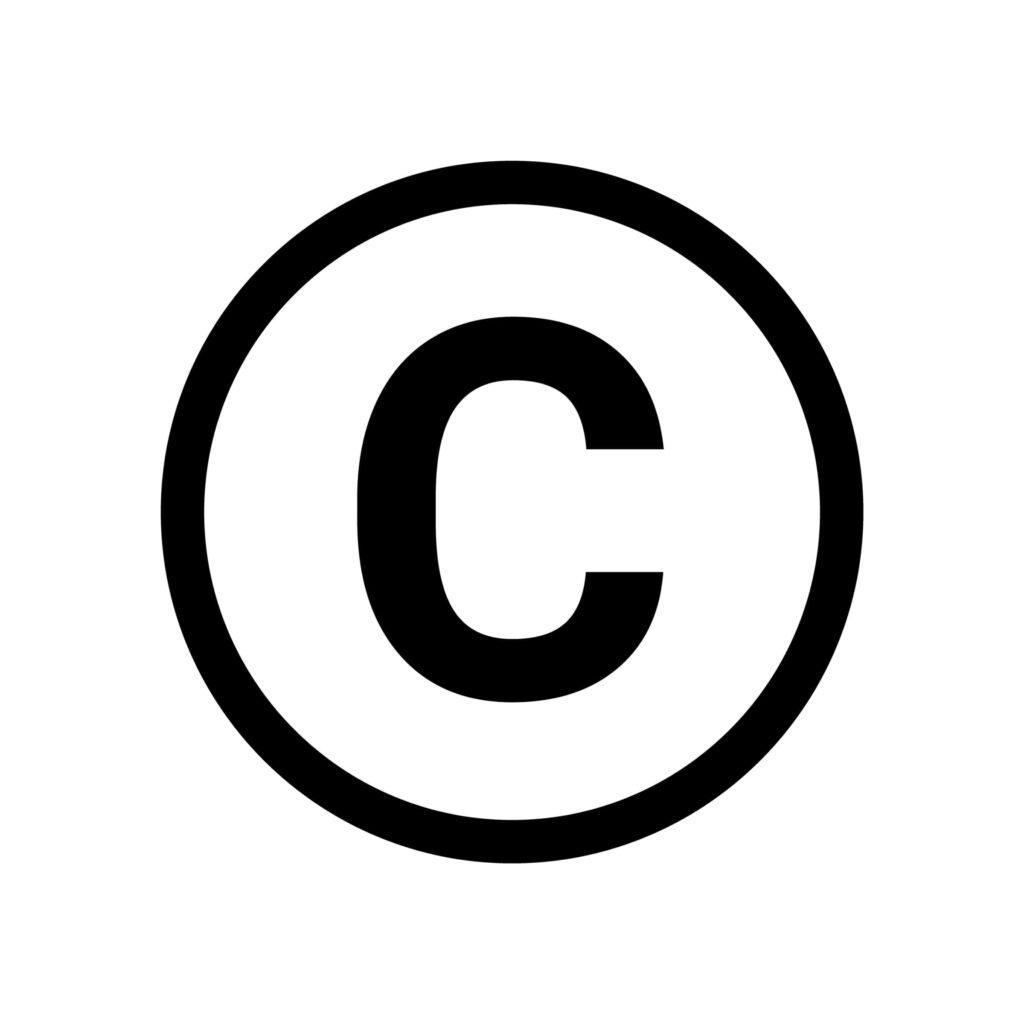 | The copyright symbol © signifies that a work is protected by copyright law. It indicates that the creator has exclusive rights to reproduce, distribute, and display their original work. It’s often followed by the year of first publication and the name of the copyright owner, reinforcing their legal claim to the work. |
 | The registered trademark symbol ® signifies that a trademark has been officially registered with the relevant government authority. |
 | The trademark symbol ™ indicates that you claim ownership of a word, phrase, logo, or design as a trademark or service mark, even if it hasn’t been officially registered. |
You can search for trademarked works on the USPTO website.
Why is it important to copyright and trademark your eCommerce store logo?
Registering both copyright and trademark for your logo comes with great benefits that protect your business and give you peace of mind.
Prevents copycats
Registering for copyright and trademark protection strengthens your ability to stop others from copying or using your logo without permission.
Copyright registration acts as a warning – people are much less likely to imitate legally protected branding elements.
You’ll have the legal power to sue anyone infringing on your rights and potentially get compensated for any losses. Without registering, it’s much harder to win these kinds of cases.
Exclusive ownership and protection
With copyright, you own the creative design itself and control its use. A trademark protects the logo as part of your brand identity in the marketplace. This means no one else can legally use something too similar without your approval.
Solidifies your brand image
A registered copyright and trademark make your business look more professional and trustworthy. It shows that you’re serious about protecting your brand, which attracts more customers and partners.
Check our resources on Etsy copyright infringement and consider whether you need a business license to sell on Etsy or other sales channels.
Make it happen today!
How to get a logo copyrighted or trademarked
Copyright only protects original designs, so make sure your logo is distinctive and unique.
Confirm that your logo isn’t already registered by heading to the following sites:
- For copyright: Check the public Copyright Records.
- For trademark: Search the USPTO trademark database.
If all is clear, proceed with the trademark and copyright registration process.
Copyright registration
- Register online: Access the US Copyright Office websiteand log in to the Electronic Copyright Office (eCO) Registration System.
- Choose application type: Select the Single Application ($45) or the Standard Application ($65), depending on your needs.
- Complete the form: Provide all the required details about your logo design and select Work of the Visual Arts in the Type of Work section.
- Submit payment: Pay the filing fees based on your application type. Additional fees may apply for specific cases.
- Processing time: Expect to wait between1 to 3.5 monthsfor standard applications and around 6 months or more if additional information is needed.
Trademark registration
- File your trademark application: Submit your application online through the trademark electronic application system on the USPTO website.
- Pay the filing fee: The cost ranges from $250 to $350 per class of goods or services.
- Processing time: The federal registration process typically takes 12 to 18 months and includes a potential opposition period.
Note that you must submit a separate application for international protection through the Madrid Protocol.
Enforcing your copyright and trademark rights

Once your registration is complete, it’s up to you to monitor any violations and take action.
Here are some tips on how to proceed in case of copyright or trademark infringement:
- Gather evidence: Save screenshots, links, or physical copies of anything showing unauthorized usage of your trademarked logo or design. Note when and where this occurred, and make sure your copyright notice is clearly visible on your work to strengthen your case.
- Contact the infringer: Reach out to whoever is using your work and explain the situation. Politely ask them to stop, as this alone can sometimes resolve the issue.
- Seek professional assistance: If the person doesn’t respond or refuses to resolve the issue, contact an intellectual property or trademark attorney. They can help you decide the next steps, whether it’s sending a formal cease and desist letter or taking legal action in federal court.
What can’t you copyright?
While copyright law covers a variety of original works, not all logos and concepts can be copyrighted. Here’s what falls outside of copyright protection.
Common knowledge
Information that’s widely known can’t be copyrighted. No one can claim ownership of facts such as:
- The Earth orbits the Sun.
- The dates of the Civil War.
- Water boils at 212°F (100°C).
Unfixed work
For something to be copyrighted, it needs to be “fixed” – meaning it has to exist in a tangible medium that people can see, touch, or interact with. Simply having an idea isn’t enough.
For example, if you’ve sketched out several ideas for a logo design, you can’t copyright them until you actually put them on paper or save them digitally. Once your idea is drawn or saved on a computer, it becomes something that can be protected.
Ideas, methods, and systems
Trademark and copyright laws don’t protect ideas, methods, or business processes. These are typically covered by patent law. Examples include:
- Business procedures and models, like print-on-demand.
- Mathematical principles, formulas, or algorithms, such as the Pythagorean theorem.
- Concepts and processes, such as the industrial assembly line.
- Scientific discoveries, like the law of gravity.
- Recipes, such as your family’s casserole.
Names, titles, and slogans
When you create a catchy brand slogan for your business, head straight to the trademark office – copyright protection doesn’t cover slogans, names, and titles.
Many of these instances are protected by other intellectual properties like trademarks or patents. Consult with an intellectual property attorney to see if your creation qualifies.
FAQs
Register to copyright your logo with the United States Copyright Office and trademark a logo by filing with the USPTO. Although your logo is automatically protected by copyright lawfor free once it’s fixed in a tangible form, registering copyright offers legal safeguards. It also provides grounds for legal action in case of unauthorized use.
The registration fee for a logo copyright differs depending on your location and the type of original work. In the United States, you can submit a logo copyright claim online for a $45 filing fee if you qualify for the Single Application.
If you register with the United States Copyright Office, the application process takes 1 to 3.5 months or more if additional supporting documents are needed. Processing times can vary, so it’s essential to keep tabs on your application.
In contrast, federal trademark registration through the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) takes over a year (usually 12 to 18 months) due to the more complex review process and potential opposition period.
You cannot copyright an online business name. Copyright law only protects original creative works, like logos, designs, or written content – not names, titles, or slogans. However, a business owner can file a trademark application with the USPTO to protect the business name from unauthorized use.
Most original works can be copyrighted, but there are exceptions. Here are some things that fall outside of copyright protection:
- Logos that are too simple or lack creativity.
- Business names, product titles, and slogans.
- Ideas, methods, and inventions.
- Common knowledge, data, and facts.
- Procedures, methods, and recipes.
To protect your company’s name or slogan, head to the USPTO website for trademark registration.
Wrapping up
Knowing how to copyright a logo is crucial for legally protecting your brand’s creative identifier. Create a fantastic logo using original artwork and submit it to the United States Copyright Office through their online portal or by paper application.
Once registered, your original logo will have enhanced copyright protection, confirming your ownership of its creative design.
Remember, while copyright protects the design elements, you should also trademark your logo at the intellectual property office to safeguard your brand’s identity and usage in the marketplace.
Do you have a POD shop and want to keep it copyright-compliant? Check out our blog on how to avoid copyright infringement in Print on Demand.